- Arctic sea ice may be thinning twice as fast as previously thought, scientists say
- The discovery raises concerns that parts of the region could be ice-free by 2040
- It would cause global temperatures to rise and increase risk of extreme weather
- Previous snow data was outdated and relied on Soviet expedition measurements

Concerning: Sea ice in much of the Arctic may be thinning twice as fast as previously thought, scientists fear. The research vessel Polarstern is pictured drifting in Arctic sea ice
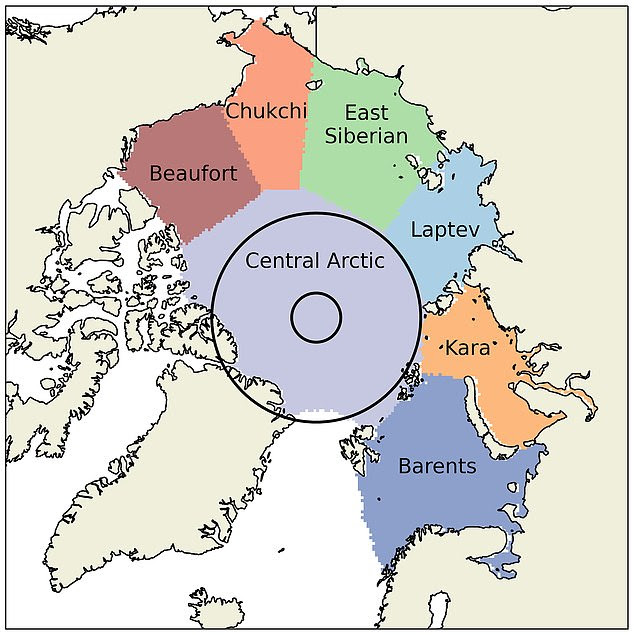
Arctic seas: Researchers studied sea ice thickness in all seven Arctic coastal seas (pictured). In Laptev, Kara and Chukchi, waters increased by 70 per cent, 98 per cent and 110 per cent respectively, when compared with earlier calculations
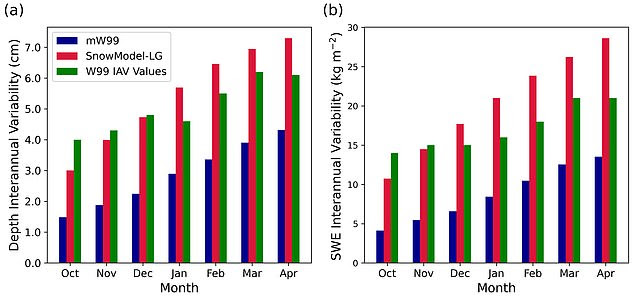
Calculations: Researchers used new computer models to produce detailed snow cover estimates from 2002 to 2018 (pictured in red). These are more accurate than previous data from Soviet expeditions between 1954 and 1991 (green) and a modified version of these recordings which account for changes in sea ice throughout the year (blue)

SEA LEVELS COULD RISE BY UP TO 4 FEET BY THE YEAR 2300
பூகோளச் சூடேற்றத்தால் மாறும் கடல் மட்ட உயர்ச்சி, தாழ்ச்சி நிகழ்வுகள்
பூகோளக் காலநிலை மாற்றங்கள் புவியின்பனிதட்டுகளைத் தொடர்ந்து பலவீனப் படுத்தி, கடல்நீர் உஷ்ணத்தை உயர்த்தி, பனித்தட்டுகளும், க்டலும் ஒன்றை ஒன்று பாதித்து, உலக மாந்தருக்கு, காலநிலைச் சுழல்வீக்க விளைவை [Climate Domino Effect] உண்டாக்கியுள்ளன. இந்த புதிய காட்சிகளைப் புவித்தளக் கொந்தளிப்பு விளைவு [Earth System Dynamic] என்னும் புத்தகம் வெளியிட்டுள்ளது.
2300 ஆண்டு காலத்தில் கடல்நீர் மட்டம் 4 அடி [1.2 மீடர்] உயர்ந்து விடும் என்று அச்சம் ஊட்டுகிறது புது வெளியீடு.
2020 ஆகஸ்டு மாதம் ஜெர்மெனி நிபுணர், கீரீன்லாந்து 532 கிகா டன் [giga ton (1 gega ton = 1 X10^9 ton] பனிப் பளுவை இழந்துள்ளது என்று அறிவித் துள்ளார். இதுபோல் பேரளவு பனிப்பளு உருகி இழக்கப் படவில்லை என்றும் கூறியுள்ளார்.
- மெலிந்து போகும் வடதுருவக் கடற்பனித் தட்டுகள் காலநிலைச் சூடேற்றச் சுழல்வீக்க விளைவினை உண்டாக்கும்.
- ஆய்வாளர் மேற்கு அண்டார்க்டிகா, கிரீன்லாந்து, சூடான அட்லாண்டிக் வெப்ப ஓட்டப் பகுதி,, அமேசான் பெருமழைக் காடுகளை எடுத்துக்கொண்டார்.
- ஏறக்குறைய மூன்றில் ஒரு பகுதி, 2 டிகிரி செல்சியஸ் உஷ்ண உயர்ச்சிக்கு, மூன்று மில்லியன் கணனிப் போலிக் கணிப்புகள் [Computer Simulations] சூடேற்ற சுழல்வீக்கத்தை உறுதிப் படுத்தின.
- 2017 ஆண்டு முடிவு வரை, சுமார் 40% உலக ஜனத்தொகை கடற்கரை ஓரத்தில்தான் வாழ்ந்து பாதிக்கப் பட்டுளார்.
Information:
- வெண்முரசு ஆவணப்படம் – வளைகுடாப் பகுதி மற்றும் கனெக்டிகட்
- சொல்வனம் 248 ஆம் இதழ் வெளியீடு அறிக்கை
- துவாரகை
- வடதுருவக் கடற்பனிப் பரப்பளவு முந்தைய கணிப்பை விட இரண்டு மடங்கு சுருங்கி விட்டது.
- அக்னிப்பிரவேசம் !
- தில்லிகை | சூன் 12 மாலை 4 மணிக்கு | மாணவர்களிடையே இலக்கியத்தின் தாக்கம்
- கொரோனா கற்றுக் கொடுத்த வாழ்வியல்
- தலைவியும் புதல்வனும்
- குழந்தைகளை உயரத்தில் வைத்துப் பார்க்கும் நிலை வரவேண்டும் !
- இல்லத்தரசி – உருது மூலம் –இஸ்மத் சுக்தாய்
- 3.ஔவையாரும் விநாயகப் பெருமானும்
- கண்ணதாசன்
- இவளும் பெண் தான்


