 NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope – https://www.
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope – https://www.
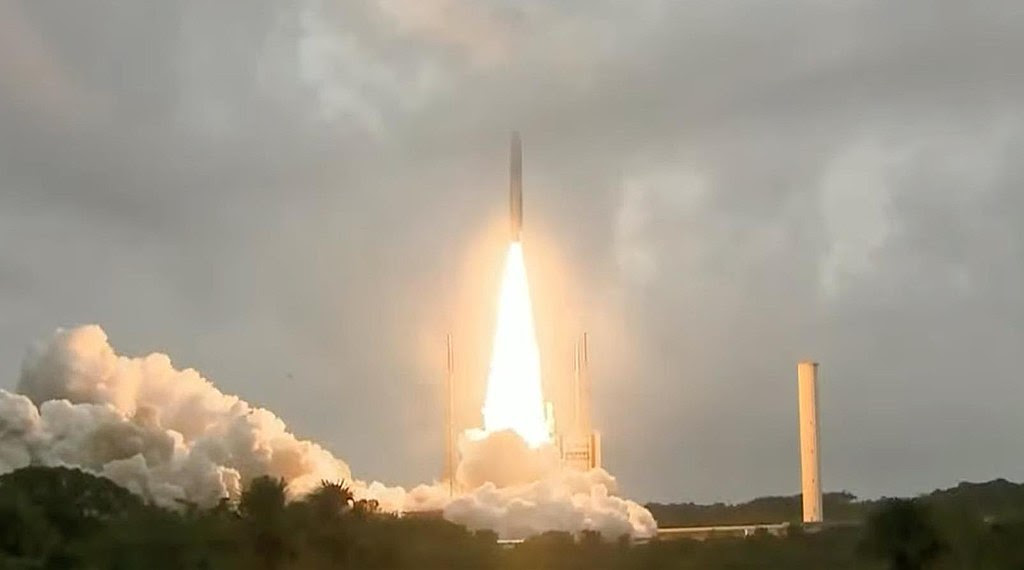
Arianespace’s Ariane 5 rocket launches with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, from the ELA-3 Launch Zone of Europe’s Spaceport at the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo credit: NASA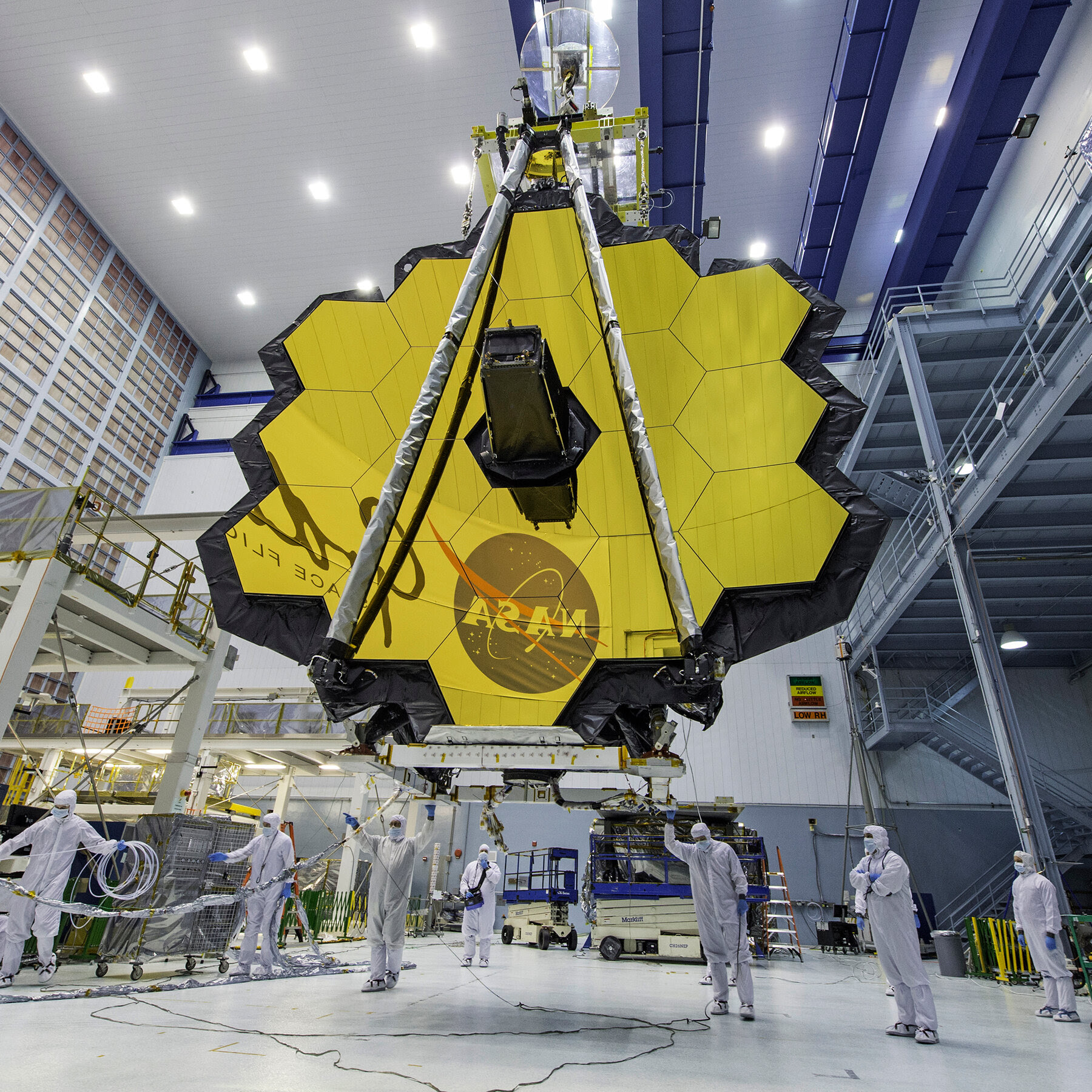 The James Webb Space Telescope is a space telescope developed by NASA with contributions from the European Space Agency, and the Canadian Space Agency. The telescope is named after James E. Webb, who was the administrator of NASA from 1961 to 1968 and played an integral role in the Apollo program. Wikipedia
The James Webb Space Telescope is a space telescope developed by NASA with contributions from the European Space Agency, and the Canadian Space Agency. The telescope is named after James E. Webb, who was the administrator of NASA from 1961 to 1968 and played an integral role in the Apollo program. Wikipedia

Comparison of Webb with Hubble Primary Mirrors
முப்பெரும் விண்வெளி நிறுவங்கள் ஒப்பற்ற ஒரு பெரும் விண்வெளி ஆய்வு தொலைநோக்கியை ஏவி உள்ளன.
2022 ஜனவரி 8 ஆம் தேதி காலை 7:20 மணிக்கு, நாசா, ஈசா, சீசா [ NASA, ESA, CSA] [NATIONAL AERONAUTICAL & SPACE ADMINISTRATION, EUROPEAN SPACE AGENCY, CANADIAN SPACE AGENCY] ஜேம்ஸ் வெப் எனப் பெயர் பெறும் பெரும் தொலைநோக்கியை, [James Webb Telescope] ஈசா ஏவுதளம் பிரென்ச் கயானாவி லிருந்து ஏரியான்-5 ராக்கெட்டில் ஏந்தி, பூமியைச் சுற்றி ஆய்வு செய்ய வெற்றி கரமாக அனுப்பி உள்ளது. இப்போது இயங்கி வரும் ஹப்பிள் தொலைநோக்கி துவங்கிய அண்டவெளித் தேடலை, வெகு தூர ஒளிமந்தைகள் [GALAXIES] ஆய்வை, தூரத்து உலகங்கள் அமைப்பை, ஜேம்ஸ் வெப் தொலை நோக்கி தொடரும். அப்பெரும் பணிகளை உலக முப்பெரும் விண்வெளி நிறுவகங்கள் ஒன்று கூடி, பூர்வீகப் பேபி பிரபஞ்சம், முதல் ஒளிமந்தை, நமது சூரிய மண்டலம், அண்டைச் சூரிய மண்டலக் கோள்கள் ஆகிய வற்றின் தோற்றங்களை ஆய்வு செய்ய தங்க முலாம் பூசிய 21 அடி முதன்மைக் கண்ணாடி உள்ளது..
ஏவிய 27 நிமிடத்தில் விண்வெளி நோக்கச் சிமிழ் ஏரியன்-5 ராக்கெட்டிலிருந்து பிரிந்து, பூமியிலிருந்து சுமார் 870 மைல் [1400 கி.மீ.] உயரத்தில் பூமியைச் சுற்ற ஆரம்பித்தது. அடுத்த மூன்று நிமிடத்தில், வெப் தொலைநோக்கியின் சூரியத் தட்டுகள், விரிந்து விண்சிமிழ் சூரிய சக்தியில் இயங்கியது.
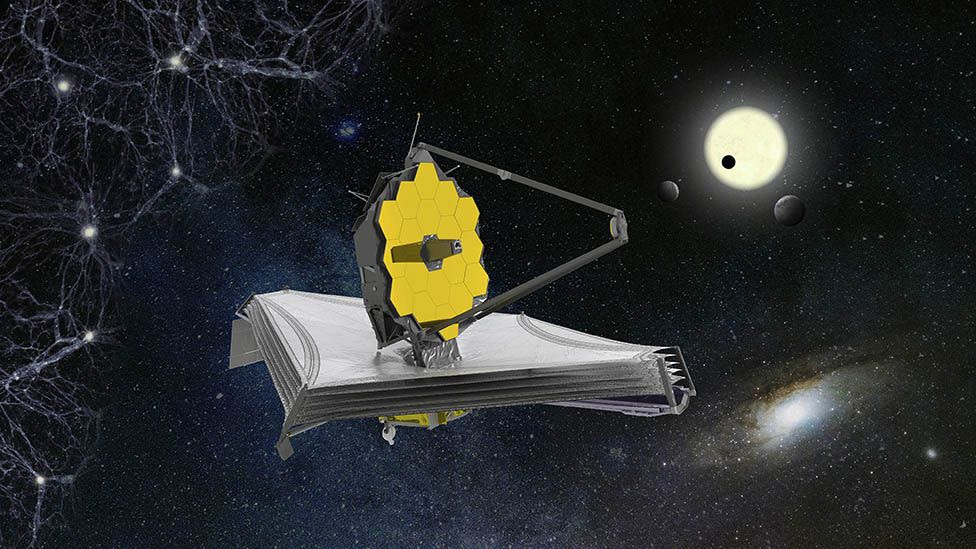 An artist’s view of the James Webb Space Telescope
An artist’s view of the James Webb Space Telescope
| A rendering of the James Webb Space Telescope with its components fully deployed. | |
| NAMES | Next Generation Space Telescope (NGST; 1996–2002) |
|---|---|
| MISSION TYPE | Astronomy |
| OPERATOR | STScI (NASA)[1] |
| COSPAR ID | 2021-130A |
| SATCAT NO. | 50463[2] |
| WEBSITE | Official website |
| MISSION DURATION | 10 years (planned)15 days (elapsed) |
| SPACECRAFT PROPERTIES | |
| MANUFACTURER | Northrop GrummanBall AerospaceL3Harris[1] |
| LAUNCH MASS | 6,161.4 kg (13,584 lb)[3] |
| DIMENSIONS | 20.197 m × 14.162 m (66.26 ft × 46.46 ft), sunshield |
| POWER | 2 kW |
| START OF MISSION | |
| LAUNCH DATE | 25 December 2021, 12:20 UTC |
| ROCKET | Ariane 5 ECA (VA256) |
| LAUNCH SITE | Centre Spatial Guyanais, ELA-3 |
| CONTRACTOR | Arianespace |
| ORBITAL PARAMETERS | |
| REFERENCE SYSTEM | Sun–Earth L2 orbit |
| REGIME | Halo orbit |
| PERIAPSIS ALTITUDE | 250,000 km (160,000 mi)[4][5][failed verification] |
| APOAPSIS ALTITUDE | 832,000 km (517,000 mi) |
| INCLINATION | 4.0560[2] |
| PERIOD | 6 months |
| MAIN TELESCOPE | |
| TYPE | Korsch telescope |
| DIAMETER | 6.5 m (21 ft) |
| FOCAL LENGTH | 131.4 m (431 ft) |
| FOCAL RATIO | f/20.2 |
| COLLECTING AREA | 25.4 m2 (273 sq ft)[6] |
| WAVELENGTHS | 0.6–28.3 μm (orange to mid-infrared) |
| TRANSPONDERS | |
| BAND | S-band, telemetry, tracking, and controlKa-band, data acquisition |
| BANDWIDTH | S-band up: 16 kbit/sS-band down: 40 kbit/sKa-band down: up to 28 Mbit/s |
| INSTRUMENTS | |
| FGS-NIRISSMIRINIRCamNIRSpec | |
| ELEMENTS | |
| Integrated Science Instrument ModuleOptical Telescope ElementSpacecraft (Bus and Sunshield) | |
James Webb Space Telescope mission logo |
தகவல் :
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/
James_Webb_Space_Telescope - https://www.space.com/nasa-
james-webb-space-telescope- launch-success - https://www.nasa.gov/press-
release/nasa-sets-coverage- invites-public-to-view-webb- telescope-launch - https://www.bbc.com/news/
science-environment-59419110
S. Jayabarathan [January 9, 2022] [R-0]
- சொல்வனம் இணையப் பத்திரிகையின் 262 ஆம் இதழ்
- காற்றுவெளி தை (2022) மின்னிதழ்
- இரண்டு பார்வைகள் !
- வந்தேறி
- பாடறிந்து ஒழுகு …
- தைப்பொங்கல் தமிழர்களின் திருநாள்
- சிறுவர் நாடகம்
- எமிலி டிக்கின்ஸன் கவிதைகள்
- அவஸ்தை
- ஆனாலும் காத்துக் கொண்டிருக்கிறேன்!
- ‘ரிஷி’(லதா ராமகிருஷ்ணன்)யின் கவிதைகள்
- நாசா, ஈசா, சீசா முப்பெரும் விண்வெளி நிறுவகங்கள் மிகப்பெரும் விண்வெளித் தொலைநோக்கியை ஏவி உள்ளன
- விடுதலை இந்தியாவில் விஞ்ஞானத் தமிழ் வளர்ச்சி
- ஒரு கதை ஒரு கருத்து
- கவிதை
MISSING YOU-TUBE VIDEOS :
1. https://youtu.be/IBPNi7uGgWM
2. https://youtu.be/7nT7JGZMbtM
LANCH DATE CORRECTION :
Arianespace’s Ariane 5 rocket launches with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, from the ELA-3 Launch Zone of Europe’s Spaceport at the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana.
CORRECT AS BELOW
SATURDAY JANUARY 8, 2022
LUANCH DATE CORRECTION :
Arianespace’s Ariane 5 rocket launches with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, Saturday, Dec. 25, 2021, from the ELA-3 Launch Zone of Europe’s Spaceport at the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana.
CORRECT AS BELOW
SATURDAY JANUARY 8, 2022
புதிய செய்தி
ஜேம்ஸ் வெப் தொலை நோக்கி இப்போது பூமியிலிருந்து ஒரு மில்லியன் மைல் தூரத்தில், பூமியோடு சேர்ந்து, ஒரு நேர் கோட்டில் சூரியனைச் சுற்றி வருகிறது.
Webb Space Telescope
Posted byLaura DattaroNovember 28, 2011
On Thursday, November 17, 2011, the House and Congress came to an agreement for the fiscal year 2012 budget that includes funding for NASA and approves the full requested funding for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), the successor to the magnificent Hubble Space Telescope. The Webb, which came under fire in July 2011 when the House proposed cutting its funding entirely, will receive $529.6 million, the amount required for it to stay on track for its planned 2018 launch.
Here are five cool things – which you might not know – about the JWST project.
1. The James Webb will unfold in space. It’s being launched on an Ariane 5 rocket, provided by the European Space Agency (ESA). But because of its massive size — it’s as big as a tennis court and about 40 feet (12 meters) high — it must be folded up for the trip. Many features of the telescope, such as the hexagonal shape of the mirrors, were designed to enable the unfolding process. Check out the video below for a glimpse of how Webb’s unfolding will take place.
2. The Webb will be nearly 1 million miles from Earth. To be exact, it’ll be 940,000 miles (about 1.5 million kilometers) from Earth.
Webb will orbit at the Second Lagrangian Point. Credit: NASA
It’s being sent to what’s known as the L2 – the second Lagrangian point in the Earth/sun system. The Lagrangian points are named for Joseph Louis Lagrange, who realized that there would be stable or semi-stable points in the vicinity of every two orbiting bodies in space. In other words, every time you have two orbiting bodies, you also get five Lagrangian points. At these points, a third body can maintain a relatively stable orbit without the heavy usage of thrusters and propellants. In this case, the sun and Earth are the two bodies in space. The Webb Telescope will orbit the L2 point in the Earth/sun system, which means it will follow Earth around the sun, always in a straight line with the Earth and sun. Its orbit will be far from Earth – beyond the moon’s orbit. For comparison, the Hubble Space Telescope is 380 miles away in low Earth orbit.
3. The Webb Telescope’s 18 mirrors are coated in a thin layer of 24-karat gold. Webb’s purpose is to read infrared light, the wavelength of light that is emitted by the farthest objects in the universe. Gold reflects red light better than other materials, making the mirror 98 percent reflective, rather than the 85 percent achieved by ordinary mirrors.
Webb
4. The Webb Telescope’s science instruments will operate at temperatures near absolute zero, the theoretical temperature at which all molecular and atomic motion ceases.
Webb
Everything that exists emits infrared radiation, which is produced from the vibration of atoms. The colder something is, the less infrared it emits. Because Webb is designed to work in the infrared, but emits infrared itself, it must be kept as cold as possible to keep its interference with itself at a minimum. Webb’s massive sunshield divides the telescope into a hot side, with temperatures around 185 degrees F, and a cold side, around -388 degrees F, or 40 Kelvin. In contrast, the coldest temperature ever recorded on Earth was -129 degrees F.
5. Planning for the Webb telescope began in 1995. Just five years after Hubble launched, scientists at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Md., first envisioned what its successor would look like, knowing it would take many years to bring this vision to fruition. Now the Webb is scheduled to be launched in 2018, and it’s a safe bet that astronomers soon will begin imagining an instrument to extend our vision with a telescope even grander and more powerful than the Webb.
For more information about the ‘scope and its science, visit its web site, or check out STScI on Facebook.
Budgets for NASA and James Webb Space Telescope still undecided
Webb Telescope instrument passes test to withstand space rigors
New Pictures of Webb Telescopes
1. Present location : https://earthsky.org/upl/2011/11/james_webb_2011_1.jpg
2. Launch of Webb capsule : https://jayabarathan.files.wordpress.com/2022/01/image-1.png